题目大意:n个结点的树,每个点有个权值,现在需要在某些点上设定一个费用,要使每个结点都要被两个费用不小于权值的点的最短路径包含,最小费用是多少?
题意翻译
给定一棵包含 n 个点的树,第 i 个点的高度为 hi。你可以在这 n 个点中建任意多个塔,对于每个塔,你都可以指定其所在的点的编号及其势能。建一个势能为 e 的塔需要花费 e 枚硬币(需要保证 e>0)。
对于一个树上的点 x,我们称其接收到了信号,当且仅当在树上存在两个建了塔的点 u,v(需要保证 u≠v,但不需要保证 x≠u 或 x≠v),使得 x 在从 u 到 v 的路径上,且 min。
请求出最少需要花费多少枚硬币,才能使得树上所有点都能接受到信号。
数据范围:
– 2\leqslant n\leqslant 2\times 10^5。
– 1\leqslant h_i\leqslant 10^9。
Translated by Eason_AC
题目描述
You are given a tree with n vertices numbered from 1 to n . The height of the i -th vertex is h_i . You can place any number of towers into vertices, for each tower you can choose which vertex to put it in, as well as choose its efficiency. Setting up a tower with efficiency e costs e coins, where e > 0 .
It is considered that a vertex x gets a signal if for some pair of towers at the vertices u and v ( u \neq v , but it is allowed that x = u or x = v ) with efficiencies e_u and e_v , respectively, it is satisfied that \min(e_u, e_v) \geq h_x and x lies on the path between u and v .
Find the minimum number of coins required to set up towers so that you can get a signal at all vertices.
输入输出格式
输入格式
The first line contains an integer n ( 2 \le n \le 200\,000 ) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains n integers h_i ( 1 \le h_i \le 10^9 ) — the heights of the vertices.
Each of the next n – 1 lines contain a pair of numbers v_i, u_i ( 1 \le v_i, u_i \le n ) — an edge of the tree. It is guaranteed that the given edges form a tree.
输出格式
输入输出样例
输入样例 #1
3
1 2 1
1 2
2 3输出样例 #1
4输入样例 #2
5
1 3 3 1 3
1 3
5 4
4 3
2 3输出样例 #2
7输入样例 #3
2
6 1
1 2输出样例 #3
12说明
In the first test case it’s optimal to install two towers with efficiencies 2 at vertices 1 and 3 .
In the second test case it’s optimal to install a tower with efficiency 1 at vertex 1 and two towers with efficiencies 3 at vertices 2 and 5 .
In the third test case it’s optimal to install two towers with efficiencies 6 at vertices 1 and 2 .
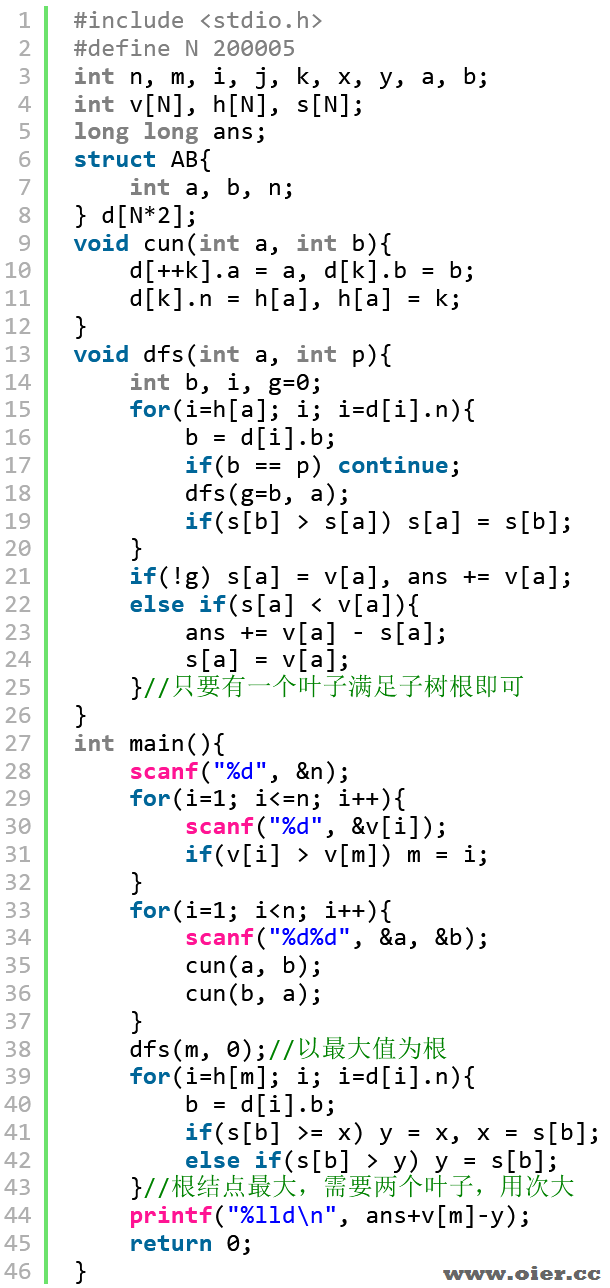
解题思路
每个点都要被包含,要么在子树内解决,要么一个在子树内,一个在外面。
什么时候在外面?外面有一个更大的点!那我们就让外面有一个更大的点,直接以最大点为根!这样,子树内只需要选择一个点不小于子树根的权值即可。
不难发现,费用都放在叶子节点,这是显而易见的贪心——往下放路径更长、费用等价。我们可以先让叶子结点的费用等于权值,从下往上,遇到更小的父亲没问题,遇到更大的父亲,则父亲需要更大的叶子,改哪个?该最大的费用差最小。
结论:以最大权值点为跟,除了根结点,每个结点只需要在子树找一个叶子满足权值即可,因为上面还有一个大权值点。根结点则需要找两个叶子节点,找最大和次大费用最小。
程序实现